Game socket
The library was published in early access and is not stable, as it is being developed in parallel with other solutions. English is not a native language so there are no comments. At this stage, the library is for those who want to understand the source code and get a starting point for their solution or help me :)
Features
- One library contains both Server and Client parts.
- The API communication library is similar to
Socket.io, but not compatible with this solution. - Contains a built-in binary protocol so you don't have to work at the byte level.
- The transport layer uses
TCP. To send game messages, it is planned to implement parallel work withUDP. - It implements such concepts as Multiplexing - interaction with several spaces through a single channel.
Support for WebSocket is not planned for the current day (but everything can change with the support of the community)
Example
Examples:
Usage
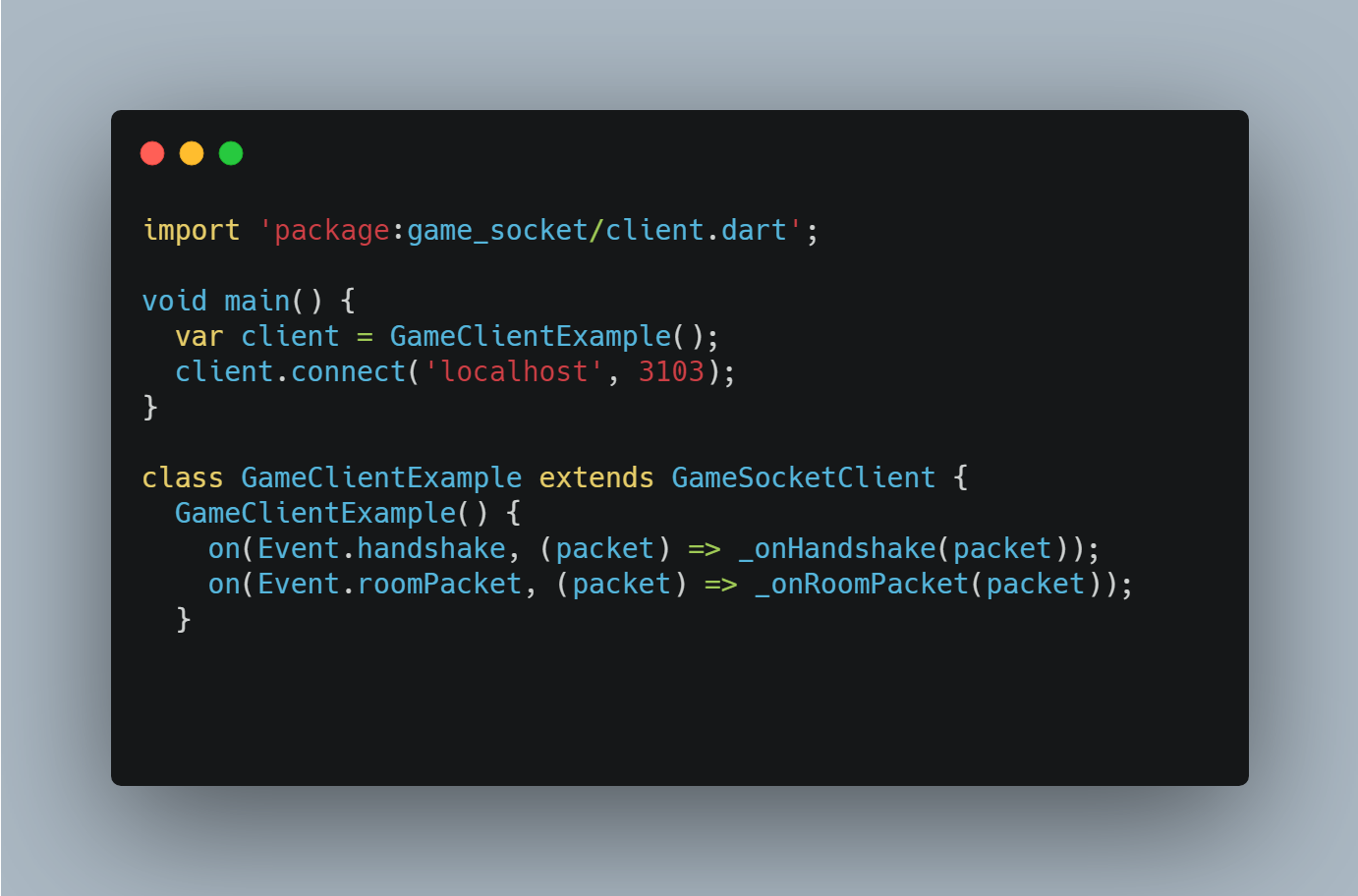
Create client:
import 'package:game_socket/client.dart';
void main() {
var client = GameClientExample();
client.connect('localhost', 3103);
}
class GameClientExample extends GameSocketClient {
GameClientExample() {
on(Event.handshake, (packet) => _onHandshake(packet));
on(Event.roomPacket, (packet) => _onRoomPacket(packet));
}
void _onHandshake(Packet packet) {
if (packet.namespace == '/') {
sendMessage(ConnectRequest('/home'));
} else if (packet.namespace == '/home') {
sendMessage(JoinRoomRequest('lobby', namespace: '/home'));
}
}
void _onRoomPacket(RoomPacket packet) {
var roomName = packet.roomName;
if (packet.joinRoom && roomName == 'lobby') {
var msg = RoomEvent(roomName!, namespace: '/home', event: 'hello', message: 'hello all');
sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
This client connects to the main / namespace on the server, then to the /home namespace. Then it sends a request to enter the lobby room, after which it dispatches a hello event containing the message text hello all.
Create server:
import 'package:game_socket/server.dart';
void main() {
var service = SocketServiceExample();
service.listen();
}
class SocketServiceExample {
late GameSocketServer server;
late Namespace home;
SocketServiceExample() {
server = GameSocketServer(options: ServerOptions.byDefault()..supportRawData = true);
home = server.of('/home');
home.on(ServerEvent.connect, (data) => _onHomeConnect(data));
home.on('hello', (packet) => _onHomeData(packet));
//
server.on(ServerEvent.connection, (socket) {
print('/: connection $socket');
socket.on(ServerEvent.connect, (data) => _onConnect(data[0], data[1]));
socket.on(Event.disconnecting, (data) => _onDisconnecting(data));
socket.on(Event.disconnect, (data) => _onDisconnect(data[0], data[1]));
socket.on(Event.error, (data) => _onError(data));
socket.on(Event.data, (data) => _onData(data));
socket.on(Event.close, (data) => {_onClose(data)});
});
server.on(ServerEvent.error, (data) => {print('/: eventError $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.close, (data) => {print('/: serverClose $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.raw, (data) => {print('/: raw $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.createRoom, (data) => {print('/: createRoom $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.joinRoom, (data) => {print('/: joinRoom $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.leaveRoom, (data) => {print('/: leaveRoom $data')});
server.on(ServerEvent.deleteRoom, (data) => {print('/: deleteRoom $data')});
}
void listen() {
server.listen();
}
void _onHomeConnect(dynamic data) {
print('/home: connect $data');
}
void _onHomeData(dynamic data) {
print('/home: $data');
if (data is RoomPacket && data.roomName != null) {
home.broadcast(data, rooms: {data.roomName!});
}
}
void _onConnect(String namespace, String socketId) {
print('/: connect $socketId');
}
void _onDisconnecting(dynamic data) {
print('/: disconnecting $data');
}
void _onDisconnect(String namespace, String reason) {
print('$namespace: disconnect reason:$reason');
}
void _onError(dynamic data) {
print('/: error $data');
}
void _onData(dynamic data) {
print('/: $data');
}
void _onClose(dynamic data) {
print('/: close $data');
}
}
Server log
listen null Options{ port:3103 raw:true closeOnError:false }
/: connection GameClient{ 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8 ReadyState.open [137545126]}
/: createRoom 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8
/: joinRoom [15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8, 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8]
Home: connect [/home, 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8]
Client log
open InternetAddress('127.0.0.1', IPv4) ReadyState.open
handshake Packet{[0.0 /], bit:516, bool:16, int:[0, 0, 60, 0, 0, 0], string:{3: 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8}}
>> Message{[/home] boolMask:4, int:[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], string:{} null}
handshake Packet{[0.0 /home], bit:516, bool:16, int:[0, 0, 60, 0, 0, 0], string:{3: 15466abe2006464e99b6c8b36f7f4ed8}}
>> Message{[/home] boolMask:16, int:[0, 0, 0], string:{0: lobby} null}
>> Message{[/home] boolMask:512, int:[0, 0, 0], string:{0: lobby, 5: hello, 1: hello all} null}
Protocol
The protocol is schematic based. This approach allows you to save the amount of data transferred, since the data type is not transferred with the message, and the length of the numbers is not serialized.
Data types used in the schema
| Type | Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| bool | 1 bit | true or false |
| int8 | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| int16 | 2 bytes | 0 to 65535 |
| int32 | 4 bytes | 0 to 4294967295 |
| string | 1 + value | 0 to 255 chars |
| bytes | 2 + value | 0 to 65535 bytes |
Schema creation
import 'package:game_socket/protocol.dart';
typedef PS = PlayerStateSchema;
class PlayerStateSchema extends SimpleSchema {
@override
int get code => 10; // unique schema code 10..255
@override
int get version => 1; // version 0..255 to support game clients with different versions
// bool
static const int reserved = 0; // reserved
@override
int get boolCount => 1;
// int8
static const int speed = 0; // 0.000..1.000
static const int health = 1; // max(100)
@override
int get int8Count => 2;
// int16
static const int uid = 2; // max(65535)
static const int angle = 3; // radians
static const int score = 4; // max(65535)
@override
int get int16Count => 3;
// int32
static const int elapsedTime = 5; // time for internal synchronization
static const int x = 6; // x-coordinate
static const int y = 7; // y-coordinate
@override
int get int32Count => 3;
// strings
static const int name = 0; // player name
@override
int get stringsCount => 1;
}
When you create a schema, you do two things: you take the named cell number of the array and determine the length of the array to one of the five schema data types.
Creating a message class
class PlayerStateMessage extends Message {
PlayerStateMessage(Player player, {required double elapsedTime}) : super(PS()) {
putUInt(PS.uid, player.uid);
putInt(PS.x, (player.positionBody.x * 1000).toInt()); // ~ -2000000.0000..+2000000.0000
putInt(PS.y, (player.positionBody.y * 1000).toInt());
putInt(PS.score, player.score);
putSingle(PS.speed, player.speed);
putRadians(PS.angle, player.rotationBody);
putUInt(PS.elapsedTime, (elapsedTime * 1000).toInt()); // double ms
}
}
Data types when writing or reading messages
| Operation | Schema Type | Dart Type | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| putBool | bool | bool | true or false |
| putInt | int8 | int | -128 to 127 |
| putUInt | int8 | int | 0 to 255 |
| putInt | int16 | int | -32768 to 32767 |
| putUInt | int16 | int | 0 to 65535 |
| putInt | int32 | int | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| putUInt | int32 | int | 0 to 4294967295 |
| putString | string | String | 0 to 255 chars |
| putSingle | ~int8~ | double | 0 to 1 step ~0.004 |
| putRadians | ~int16~ | double | step ~0.0002 |
| putPayload | bytes | Uint8List | 0 to 65535 bytes |
Plans
- Initialization for sending
UPDdiagrams. - Automatic connections and reconnections.
- Expanding the possibilities for working with rooms.
- Conducting stress tests.
Tips for Beginners
- If you are developing a browser game, then you need a
WebSocketsolution. - When designing a game for real-time communication,
UDPshould be preferred, sinceTCPwill cause a delay in the event of packet loss.