Mustang
A framework to build Flutter applications. Following features are available out of the box.
- State Management
- Persistence
- Cache
- File layout and naming standards
- Reduces boilerplate with open_mustang_cli
Framework Components
-
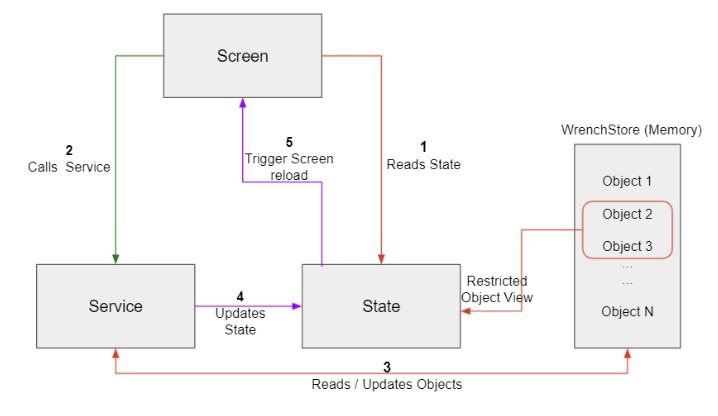
Screen – Screen is a reusable widget. It usually represents a screen in the app or a page in Browser.
-
Model – A Dart class representing application data.
-
State – Provides access to subset of
Modelsneeded for aScreen. It is a Dart class with 1 or moreModelfields. -
Service – A Dart class for async communication and business logic.
Component Communication
-
Every
Screenhas a correspondingServiceand aState. All three components work together to continuously
rebuild the UI whenever there is a change in the application state.ScreenreadsStatewhile building the UIScreeninvokes methods in theServiceas a response to user events (scroll,tapetc.,)Service- reads/updates
Modelsin theWrenchStore - makes API calls, if needed
- informs
StateifWrenchStoreis mutated
- reads/updates
StateinformsScreento rebuild the UI- Back to Step 1
Persistence
By default, app state is maintained in memory by WrenchStore. When the app is terminated, the app state is lost
permanently. However, there are cases where it is desirable to persist and restore the app state. For example,
- Save and restore user’s session token to prevent user having to log in everytime
- Save and restore partial changes in a screen so that the work can be resumed from where the user has left off.
Enabling persistence is simple and works transparently.
import 'package:xxx/src/models/serializers.dart' as app_serializer;
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
// In main.dart before calling runApp method,
// 1. Enable persistence like below
WrenchStore.config(
isPersistent: true,
storeName: 'myapp',
);
// 2. Initialize persistence
Directory dir = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
await WrenchStore.initPersistence(dir.path);
// 3. Restore persisted state before the app starts
await WrenchStore.restoreState(app_serializer.json2Type, app_serializer.serializerNames);
With the above change, app state (WrenchStore) is persisted to the disk and will be restored into WrenchStore when the app is started.
Cache
Cache feature allows switching between instances of the same type on need basis.
Persistence is a snapshot of the app state in memory (WrenchStore). However, there are times when data
need to be persisted but restored only when needed. An example would be a technician working on multiple jobs at the same time i.e, technician switches between jobs.
Since the WrenchStore allows only one instance of a type, there cannot be two instances of the Job object in the WrenchStore.
Cache APIs, available in Services, make it easy to restore any instance into memory (WrenchStore).
-
Future<void> addObjectToCache<T>(String key, T t)Save an instance of type
Tin the cache.keyis an identifier for one or more cached objects. -
Future<void> deleteObjectsFromCache(String key)Delete all cached objects having the identifier
key -
static Future<void> restoreObjects( String key, void Function( void Function<T>(T t) update, String modelName, String jsonStr, ) callback, )Restores all objects in the cache identified by the
keyinto memoryWrenchStoreand also into the persisted store
so that the in-memory and persisted app state remain consistent. -
bool itemExistsInCache(String key)Returns
trueif an identifierkeyexists in the Cache,falseotherwise.
Model
-
A Class annotated with
appModel -
Model name should start with
$ -
Initialize fields with
InitFieldannotation -
Methods/Getters/Setters are
NOTsupported insideModelclasses -
If a field should be excluded when a
Modelis persisted, annotate that field withSerializeField(false)@appModel class $User { late String name; late int age; @InitField(false) late bool admin; @InitField(['user', 'default']) late BuiltList<String> roles; late $Address address; // $Address is another model annotated with @appModel late BuiltList<$Vehicle> vehicles; // Use immutable versions of List/Map inside Model classes @SerializeField(false) late String errorMsg; // errorMsg field will not be included when $User model is persisted }
State
-
A class annotated with
screenState -
State name should start with
$ -
Fields of the class must be
Modelclasses@screenState class $ExampleScreenState { late $User user; late $Vehicle vehicle; }
Service
-
A class annotated with
ScreenService -
Provide
Stateclass as an argument toScreenServiceannotation, to create an association betweenStateandServiceas shown below.@ScreenService(screenState: $ExampleScreenState) class ExampleScreenService { void getUser() { User user = WrenchStore.get<User>() ?? User(); updateState1(user); } }
-
Service also provides following APIs
-
updateState– Updates screen state and/or re-build the screen. To update theStatewithout re-building the screen. Setreloadargument tofalseto update theStatewithout re-building theScreen.updateState()updateState1(T model1, { reload: true })updateState2(T model1, S model2, { reload: true })updateState3(T model1, S model2, U model3, { reload: true })updateState4(T model1, S model2, U mode3, V model4, { reload: true })
-
memoizeScreen– Invokes any method passed as argument only once.T memoizeScreen<T>(T Function() methodName)// In the snippet below, getScreenData method caches the return value of getData method, a Future. // Even when getData method is called multiple times, method execution happens only the first time. Future<void> getData() async { Common common = WrenchStore.get<Common>() ?? Common(); User user; Vehicle vehicle; ... } Future<void> getScreenData() async { return memoize(getData); }
-
clearMemoizedScreen– Clears value cached bymemoizeScreenmethod.void clearMemoizedScreen()Future<void> getData() async { ... } Future<void> getScreenData() async { return memoizeScreen(getData); } void resetScreen() { // clears Future<void> cached by memoizeScreen() clearMemoizedScreen(); }
-
Screen
-
Use
StateProviderwidget to re-build theScreenautomatically when there is a change inState... Widget build(BuildContext context) { return StateProvider<HomeScreenState>( state: HomeScreenState(), child: Builder( builder: (BuildContext context) { // state variable provides access to model fields declared in the HomeScreenState class HomeScreenState? state = StateConsumer<HomeScreenState>().of(context); # Even when this widget is built many times, only 1 API call # will be made because the Future from the service is cached SchedulerBinding.instance?.addPostFrameCallback( (_) => HomeScreenService().getScreenData(), ); if (state?.common?.busy ?? false) { return Spinner(); } if (state?.counter?.errorMsg.isNotEmpty ?? false) { return ErrorBody(errorMsg: state.common.errorMsg); } return _body(state, context); }, ), ); }
Folder Structure
- Folder structure of a Flutter application created with this framework looks as below
lib/ - main.dart - src - models/ - model1.dart - model2.dart - screens/ - first/ - first_screen.dart - first_state.dart - first_service.dart - second/ - second_screen.dart - second_state.dart - second_service.dart - Every
Screenneeds aStateand aService. So,Screen, State, Servicefiles are grouped inside a directory - All
Modelclasses must be insidemodelsdirectory
Quick Start
-
Install Flutter
mkdir -p ~/lib && cd ~/lib git clone https://github.com/flutter/flutter.git -b stable # Add PATH in ~/.zshrc export PATH=$PATH:~/lib/flutter/bin export PATH=$PATH:~/.pub-cache/bin
-
Install Mustang CLI
dart pub global activate open_mustang_cli
-
Create Flutter project
cd /tmp flutter create quick_start cd quick_start # Open the project in editor of your choice # vscode - code . # IntelliJ - idea .
-
Update
pubspec.yaml... dependencies: ... built_collection: ^5.1.1 built_value: ^8.1.3 mustang_core: ^1.0.2 path_provider: ^2.0.6 dev_dependencies: ... build_runner: ^2.1.4 mustang_codegen: ^1.0.3
-
Install dependencies
flutter pub get
-
Generate files for a screen called
counter. Following command creates file representing aModel, and also files representingScreen,ServiceandState.omcli -s counter
-
Generate runtime files and watch for changes.
omcli -w # omcli -b generates runtime files once -
Update the generated
counter.dartmodelclass $Counter { @InitField(0) late int value; }
-
Update the generated
counter_screen.dartscreenimport 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:mustang_core/mustang_widgets.dart'; import 'counter_service.dart'; import 'counter_state.state.dart'; class CounterScreen extends StatelessWidget { const CounterScreen({ Key key, }) : super(key: key); @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return StateProvider<CounterState>( state: CounterState(), child: Builder( builder: (BuildContext context) { CounterState? state = StateConsumer<CounterState>().of(context); return _body(state, context); }, ), ); } Widget _body(CounterState? state, BuildContext context) { int counter = state?.counter?.value ?? 0; return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('Counter'), ), body: Center( child: Column( children: [ Padding( padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0), child: Text('$counter'), ), ElevatedButton( onPressed: CounterService().increment, child: const Text('Increment'), ), ], ), ), ); } }
-
Update the generated
counter_service.dartserviceimport 'package:mustang_core/mustang_core.dart'; import 'package:quick_start/src/models/counter.model.dart'; import 'counter_service.service.dart'; import 'counter_state.dart'; @ScreenService(screenState: $CounterState) class CounterService { void increment() { Counter counter = WrenchStore.get<Counter>() ?? Counter(); counter = counter.rebuild((b) => b.value = (b.value ?? 0) + 1); updateState1(counter); } }
-
Update
main.dart... Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Flutter Demo', theme: ThemeData( ... primarySwatch: Colors.blue, ), home: CounterScreen(), // Point to Counter screen ); } ...