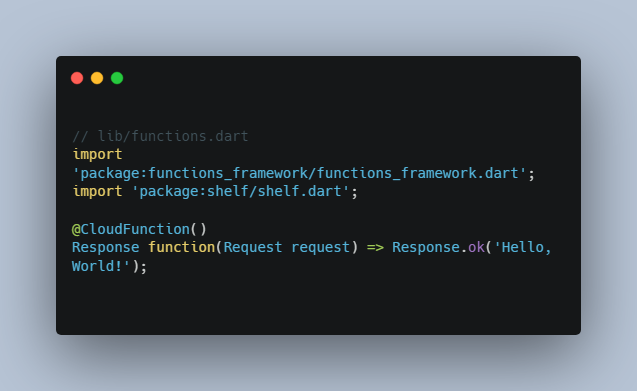
Hello world example
This example handles HTTP GET requests by responding with ‘Hello, World!’.
// lib/functions.dart
import 'package:functions_framework/functions_framework.dart';
import 'package:shelf/shelf.dart';
@CloudFunction()
Response function(Request request) => Response.ok('Hello, World!');
Simulate a hosted environment on your own machine
You can run this function example on your own machine using Docker to simulate running in a hosted environment.
$ docker build -t hello .
...
$ docker run -it -p 8080:8080 --name app hello
Listening on :8080
From another terminal:
curl http://localhost:8080
Hello, World!
If you’re curious about the size of the image you created, enter:
$ docker image ls hello
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello latest 3f23c737877b 1 minute ago 11.6MB
Editing the function and testing locally
If you would like to rename the handler function (function) to something else
(ex: handleGet), you need to ensure that the FUNCTION_TARGET environment
variable is set to the new function name.
For example:
@CloudFunction()
Response handleGet(Request request) => Response.ok('Hello, World!');
Run the build_runner to regenerate bin/server.dart from lib/functions.dart
$ dart run build_runner build
[INFO] Generating build script completed, took 304ms
[INFO] Reading cached asset graph completed, took 46ms
[INFO] Checking for updates since last build completed, took 412ms
[INFO] Running build completed, took 2.2s
[INFO] Caching finalized dependency graph completed, took 28ms
[INFO] Succeeded after 2.3s with 1 outputs (1 actions)
Run tests (note that FUNCTION_TARGET must now be set for the test process):
$ FUNCTION_TARGET=handleGet dart test
00:02 +1: All tests passed!
Run it on your system:
$ FUNCTION_TARGET=handleGet dart run bin/server.dart
Listening on :8080
If you want to test this hosted on your machine, rebuild the image
$ docker build -t hello .
...
If you had a previous container running, make sure to remove it now. Assuming
you named the container app (as demonstrated earlier):
docker rm -f app
Now launch another container, this time ensuring the environment variable is passed to Docker so that it will be set for the containerized function:
$ docker run -it -p 8080:8080 --name app -e 'FUNCTION_TARGET=handleGet' hello
App listening on :8080
Clean up
When finished, clean up by entering:
docker rm -f app # remove the container
docker image rm hello # remove the image
Makefile
If you’re familiar with make and have it in your path, you can use the
provided Makefile for convenience while developing and testing your
source code locally until ready to test in a container or deploy it. The
following targets are supported:
make build– this is the default target and will generatebin/server.dartmake clean– clears build_runner cache and removes thebin/server.dartmake test– runscleanandbuildtargets, then runs testsmake run– runs thebuildtarget and then starts the Dart function server locally